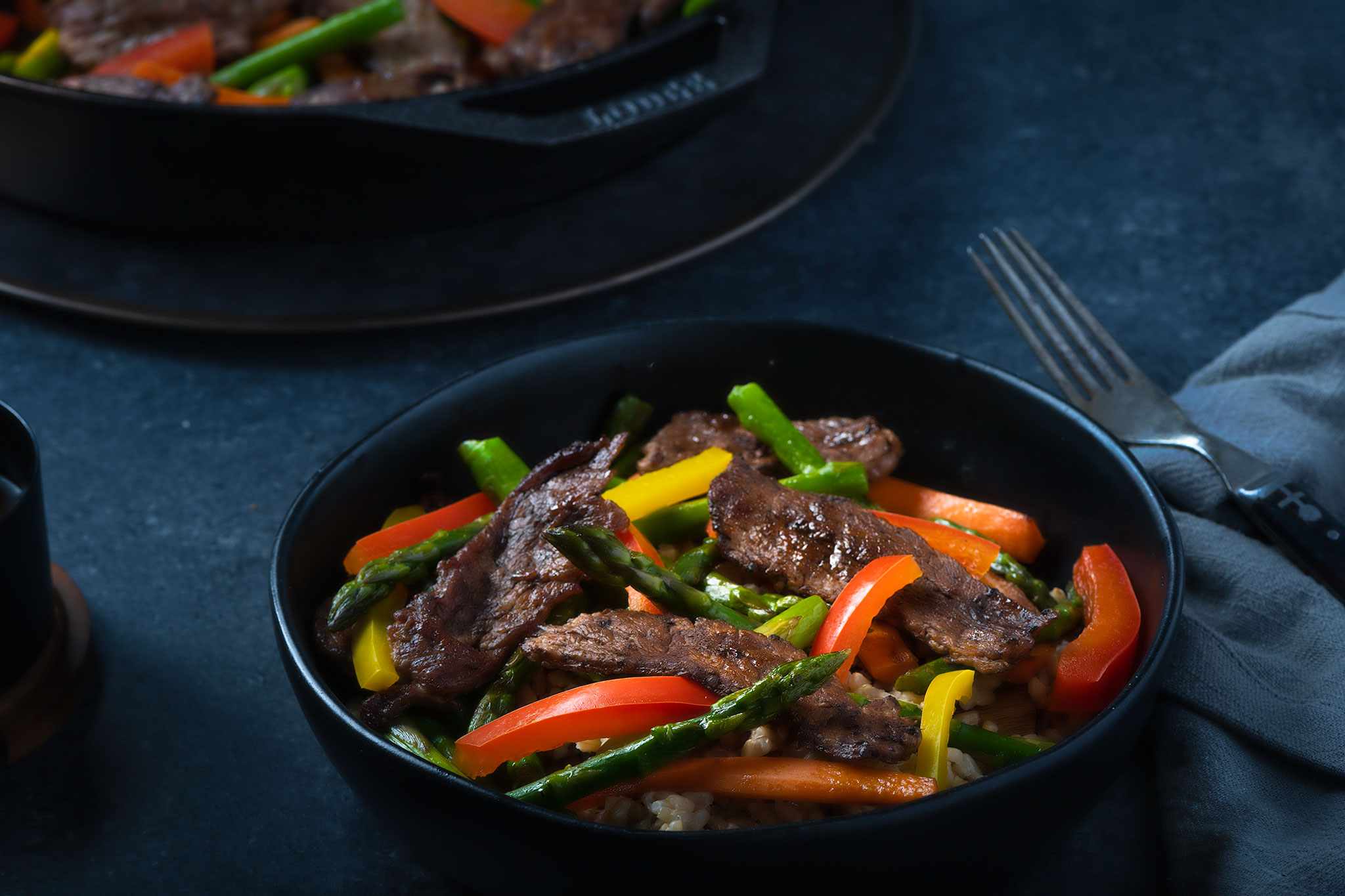
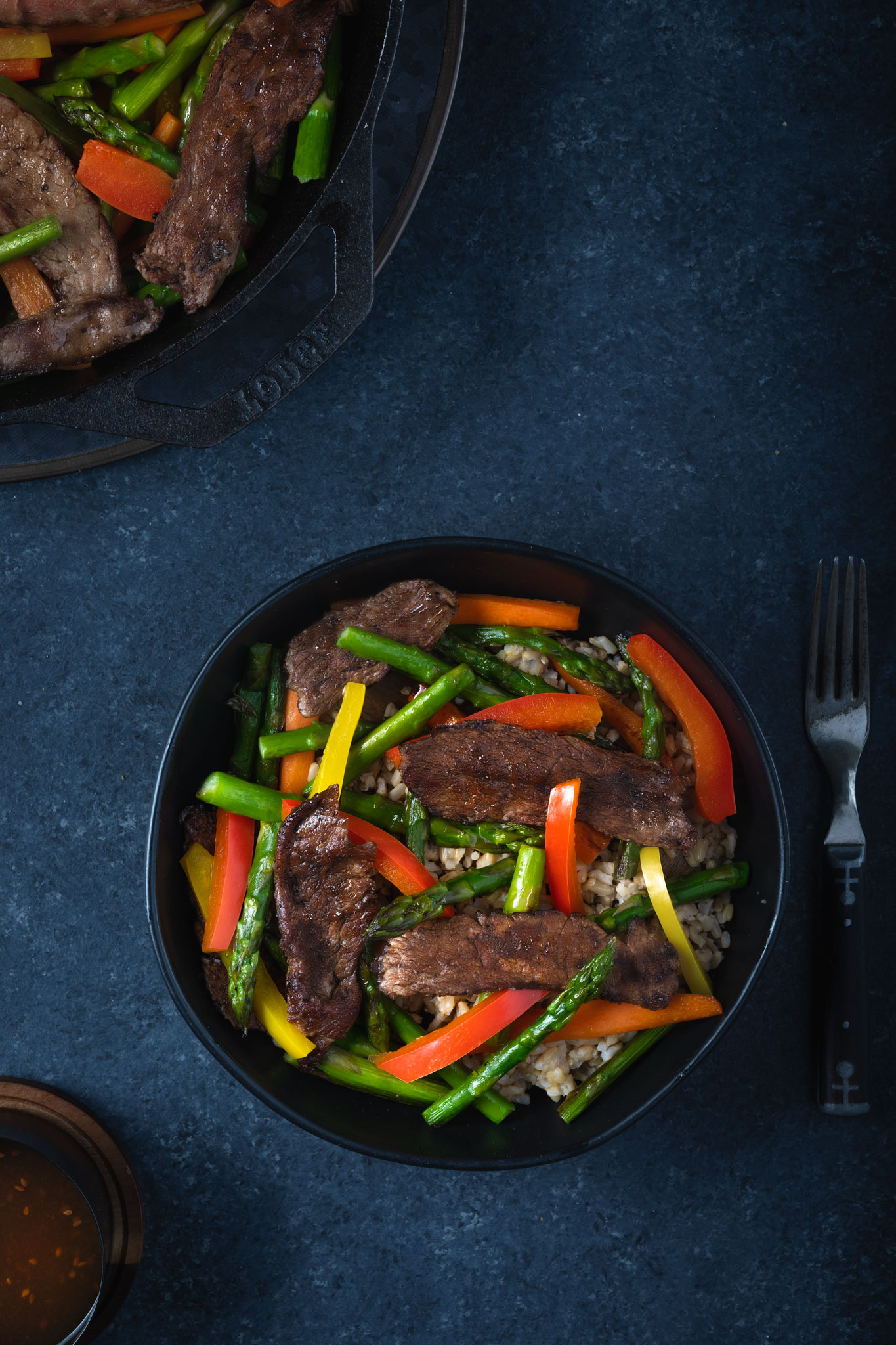
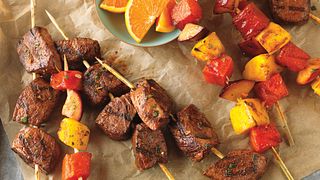balanced beef and veggie stir fry
This simple beef and veggie stir fry comes together quickly and allows you to fine-tune it to your liking by using your favorite store-bought Teriyaki sauce.
We love this recipe because it's easy, delicious and definitely nutritious. Nutrient-rich beef brings more to the table when paired with fruits and vegetables as part of a healthy, balanced diet because the nutrients in beef and produce compliment each other. For example, the iron in beef, which is more easily absorbed than iron from plant sources, receives a boost in absorption when combined with vitamin C from bell peppers1,2,3. Also, small amounts of fat from beef help improve the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin A found in carrots and vitamin K found in asparagus and snow peas4. Fruits and vegetables combined with lean beef pack-in an abundance of flavor and nutrients per calorie, making them an ideal pair for your plant-forward plate.

- Time: 20-30 minutes
- Serves 4
Ingredients
- 1 lb Flank Steak
- 1.5 tbsp avocado oil
- 2 cloves garlic
- 2 medium carrots, cut into match sticks
- 1/2lb asparagus, sliced into 1" pieces
- 1 red bell pepper, cut into strips
- 1 yellow bell pepper, cut into strips
- 6 oz snow peas, cut in half on a bias
- 2 tbsp sesame seeds
- Low-sodium, no-sugar-added Teriyaki sauce.
- 1 cup brown rice
Instructions
1. Place Flank Steak in plastic bag and place in freezer for 30 minutes. Remove, and cut into thin slices. Meanwhile, heat 1 tbsp oil in large pan on medium-high heat. Sear steak on each side in batches. Remove from pan.
2. Add remaining oil. Cook cook carrots and asparagus for five minutes. Add garlic; cook additional three minutes.
3. Add peppers, cook three minutes or until tender. Add snow peas, cook an additional two minutes.
4. Return beef to pan and add sauce to taste. Serve immediately over brown rice.
*Optional: For a more tender steak, marinate in Teriyaki sauce for at least four hours, preferably overnight.
Citations
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. Iron: Fact sheet for health professionals. Available at: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-HealthProfessional/#en2
- Hurrell R, Egli I. Iron bioavailability and dietary reference values. Am J Clin Nutr 2010;91:1461S-7S. [PubMed abstract]
- Tuecher B, Olivares M, Cori H. Enhancers of iron absorption: Ascorbic acid and other organic acids. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 2004;74(6):403-19
- Wax E, Zieve D, Conway B. (2019): Vitamins, MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. National Institutes of Health, U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved September 15, 2020 from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002399.htm