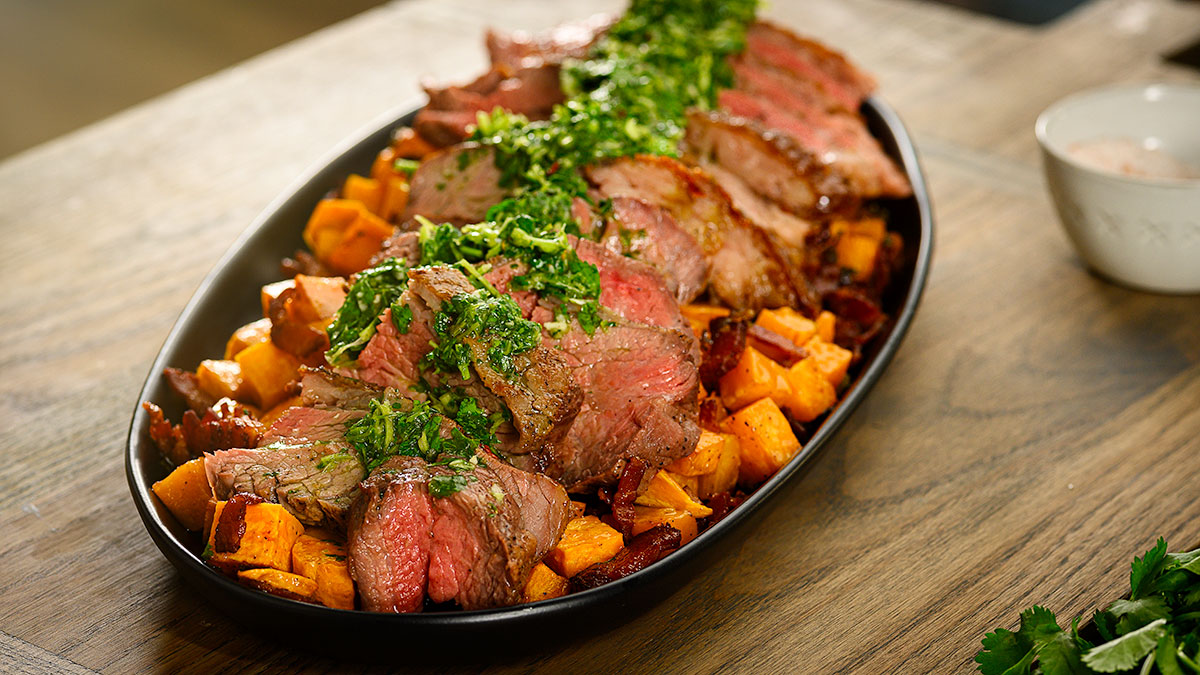
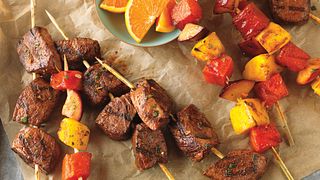7 surprising facts about beef & a heart healthy diet
Eating for a healthy heart and enjoying your favorite foods like beef don’t have to be at odds with one another. Lean beef helps support a strong body by providing important nutrients to build and replenish muscles and, among all the muscles in your body, your heart is arguably the most important. Keep it healthy by finding a balance of diet and exercise, the two cornerstones for building a strong, healthy heart. When it comes to diet, the American Heart Association recommends eating a variety of nutritious foods from all food groups for a heart-healthy diet.1 A heart-healthy diet includes an abundance of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats and lean protein.
Here are seven surprising facts about beef and a heart-healthy diet.
1. LEAN AND EXTRA-LEAN CUTS OF BEEF ARE EASY TO FIND
There are 9 extra-lean beef cuts that carry the American Heart Association’s Heart-Check certification for foods that fit in an overall heart-healthy dietary pattern. These extra-lean cuts of beef have less than 5 grams of total fat, less than 2 grams of saturated fat and less than 95 mg of cholesterol per 3.5-ounce serving. They include popular, tasty favorites like extra lean ground beef (96% lean, 4% fat), Bottom Round Steak (USDA Select grade) and Top Sirloin Steak (Boneless, Center Cut, USDA Select grade). We’ve got you covered with beef recipes certified by the American Heart Association, like this tasty Beef Pot Roast with Cider Gravy and Maple Sweet Potatoes.
2. A Mediterranean style eating pattern can include lean beef
The Mediterranean diet is one of the most popular eating patterns and is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts/seeds, olive oil and lean meats. It’s been shown that intake of red meat in many Mediterranean countries is similar to that of the United States and, in some countries, even more.2 Recent research shows a Mediterranean-style eating pattern that includes lean, unprocessed red meat can support heart health and, in fact, is just as effective at improving certain heart disease risk factors (like blood pressure, total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol).3
3. Beef contains the same type of healthy fat found in avocados and olive oil
- The delicious flavor of a steak is found in the intra-muscular fat called marbling.
- More than half the fatty acids found in beef are monounsaturated fatty acids, the same type of healthy fat found in avocados and olive oil. 4, 5
- Approximately one-third of beef’s saturated fat is stearic acid, the same fat recognized as beneficial in chocolate for its neutral effect on blood cholesterol levels. 4, 6, 7, 8
4. Lean beef is a perfect partner for fruits and vegetables
Beef and fruit? That’s right. The succulent taste of lean beef is a mouthwatering match for fruits and vegetables. These balanced beef recipes tastefully combine a variety of food groups to achieve the perfect blend of taste, nutrition and simplicity. For quick and nutritious weeknight meals, try the Beef Tenderloin, Cranberry and Pear Salad or the Szechuan Beef Stir Fry.
5. The protein in beef plays an important role in weight management
- increasing satiety (helping you stay full longer)
- helping support strong, lean bodies and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as sarcopenia, type-2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. 9, 10, 11, 12
- offering more protein with the fewest calories when compared to plant proteins like quinoa, peanut butter, black beans and edamame.13
6. Beef provides big nutrition in a small package
On average, a 3-ounce serving of cooked beef – about the size of a deck of cards – provides more than 10 essential nutrients and about half the Daily Value for protein in about 175 calories.14 These essential nutrients include
- zinc, which helps maintain a healthy immune system
- iron, which helps your body use oxygen
- vitamins B6 and B12, which help maintain brain function and give you energy.
When it comes to high-quality proteins, beef provides many nutrients in a smaller serving size than some other choices. For example, you’d have to eat at least 8 ounces of cooked chicken breast to get the same amount of iron in just 3 ounces of cooked beef. 14 Beef gives you the nutrients your body needs and the taste you love!

7. Grass-finished and grain-finished beef both can fit into a heart-healthy diet.
- Grass-finished and grain-finished beef provide similar nutritional benefits.
- All cattle, whether grass- or grain-finished, spend the majority of their lives eating grass.
- While grass-finished beef tends to be a little leaner, both grass-finished and grain-finished beef are natural sources of more than 10 essential nutrients. 15
If you want to know more about grass-finished beef, grain-finished beef and other beef choices, check out this resource about decoding beef labels.

*Heart-Check certification does not apply to recipes, links, information reached through links, or scientific studies unless expressly stated.”
sources, because we like scientific evidence.
- The American Heart Association’s Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations. (n.d.). Retrieved October 03, 2016, from http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/HealthyLiving/HealthyEating/Nutrition/The-American-Heart-Associations-Diet-and-Lifestyle-Recommendations.
- Report of the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee on the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2015. Available at https://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015-scientific-report/PDFs/Scientific-Report-of-the-2015-Dietary-Guidelines-Advisory-Committee.pdf.
- O’Connor LE, et al. A Mediterranean-style eating pattern with lean, unprocessed red meat has cardiometabolic benefits for adults who are overweight or obese in a randomized, crossover, controlled feeding trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2018, nqy075. https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/advance-article/doi/10.1093/ajcn/nqy075/5036105.
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Nutrient Data Laboratory. USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 28 (Slightly revised). Version Current: May 2016. Available at http://www.ars.usda.gov/ba/bhnrc/ndl.
- Hammad S, et al. Current evidence supporting the link between dietary fatty acids and cardiovascular disease. Lipids 2016;51:507-17.
- Denke MA. Role of beef and beef tallow, an enriched source of stearic acid, in a cholesterol-lowering diet. Am J Clin Nutr 1994;60:1044S-9S.
- Kris-Etherton PM, Mustad VA. Chocolate feeding studies: a novel approach for evaluating the plasma lipid effects of stearic acid. Am J Clin Nutr 1994;60:1029S-36S.
- Hunter JE, et al. Cardiovascular disease risk of dietary stearic acid compared with trans, other saturated, and unsaturated fatty acids: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr 2010;91:46-63.
- Roussell MA, et al. Beef in an Optimal Lean Diet study: Effects on lipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins. Am J Clin Nutr 2012;95:9-16.
- Leidy HJ, et al. The role of protein in weight loss and maintenance. Am J Clin Nutr 2015;101:1320S–9S.
- Paddon-Jones D, et al. Protein and healthy aging. Am J Clin Nutr 2015;101:1339S–45S.
- Layman DK, et al. Protein in optimal health: Heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr 2008;87:1571S-5S.
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. FoodData Central, 2019. USDA NDB ID #s: 20137-quinoa, 16097-peanut butter, 16316-black beans, 11212-edamame, 13364-composite beef. https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. FoodData Central, 2019. USDA NDB ID #s: 13364-composite beef, 05064-skinless chicken breast. https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/ .
- Van Elswyk ME, McNeill SH. Impact of grass/forage feeding versus grain finishing on beef nutrients and sensory quality: the U.S. experience. Meat Sci 2014;96:535-40.